Quickstart#
You can create an example.py to solve the classical Poisson’s equation:
import jax
import jax.numpy as np
import os
from jax_fem.problem import Problem
from jax_fem.solver import solver
from jax_fem.utils import save_sol
from jax_fem.generate_mesh import get_meshio_cell_type, Mesh, rectangle_mesh
class Poisson(Problem):
def get_tensor_map(self):
return lambda x: x
def get_mass_map(self):
def mass_map(u, x):
val = -np.array([10*np.exp(-(np.power(x[0] - 0.5, 2) + np.power(x[1] - 0.5, 2)) / 0.02)])
return val
return mass_map
ele_type = 'QUAD4'
cell_type = get_meshio_cell_type(ele_type)
Lx, Ly = 1., 1.
meshio_mesh = rectangle_mesh(Nx=32, Ny=32, domain_x=Lx, domain_y=Ly)
mesh = Mesh(meshio_mesh.points, meshio_mesh.cells_dict[cell_type])
def left(point):
return np.isclose(point[0], 0., atol=1e-5)
def right(point):
return np.isclose(point[0], Lx, atol=1e-5)
def bottom(point):
return np.isclose(point[1], 0., atol=1e-5)
def top(point):
return np.isclose(point[1], Ly, atol=1e-5)
def dirichlet_val(point):
return 0.
location_fns = [left, right, bottom, top]
value_fns = [dirichlet_val]*4
vecs = [0]*4
dirichlet_bc_info = [location_fns, vecs, value_fns]
problem = Poisson(mesh=mesh, vec=1, dim=2, ele_type=ele_type, dirichlet_bc_info=dirichlet_bc_info)
sol = solver(problem)
data_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data')
vtk_path = os.path.join(data_dir, f'vtk/u.vtu')
save_sol(problem.fes[0], sol[0], vtk_path)
and run it:
python example.py
The generated result file u.vtu can be visualized with ParaView.
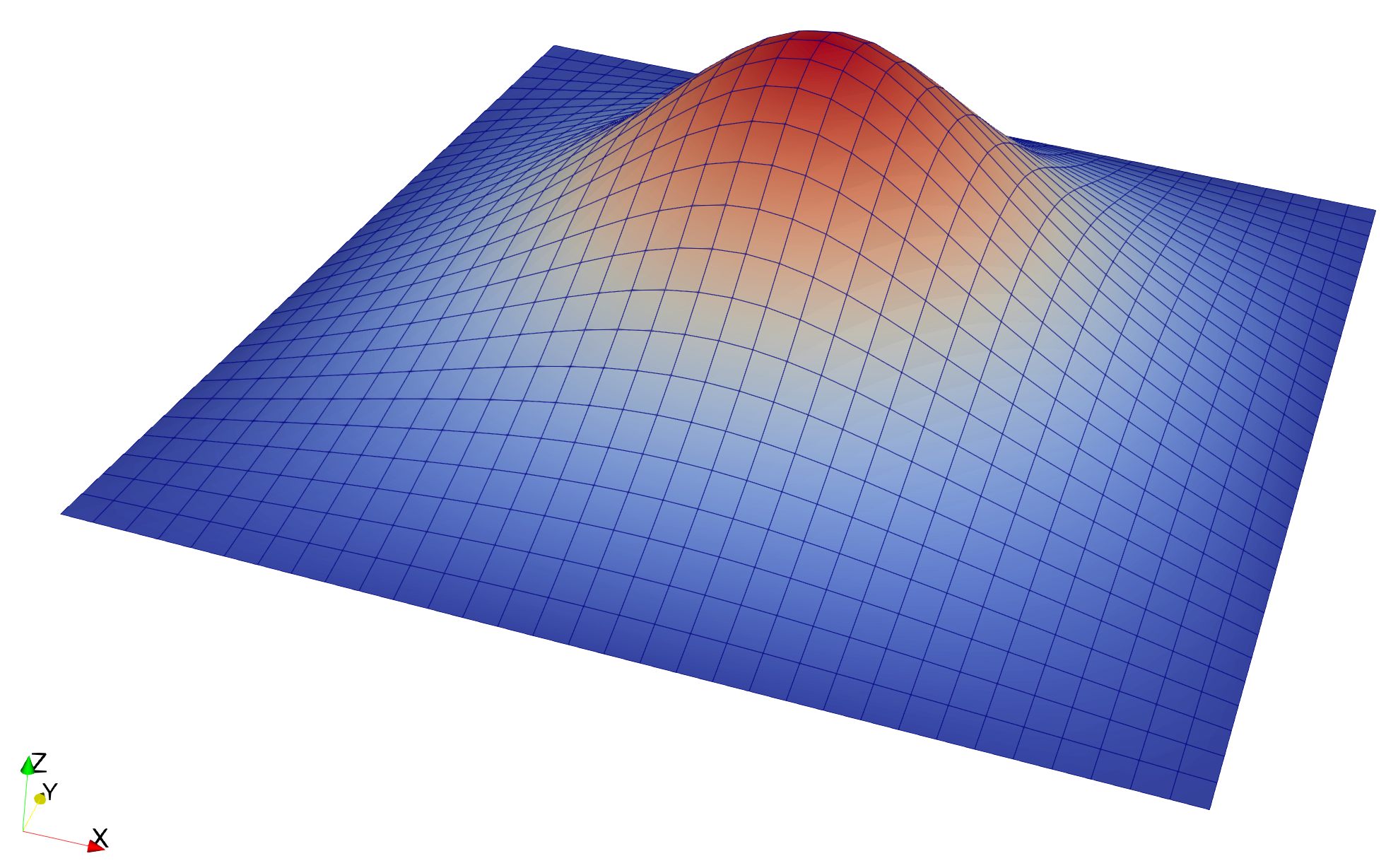
Solution to the Poisson's equation due to a source term.
